Types of resistance
Topic time estimate: 5 Minutes
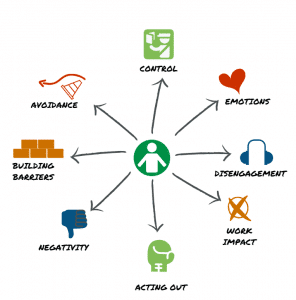
Resistance is the refusal to accept or comply with changes. It is a person’s attempt to prevent changes by action or argument. Resistance to change manifests itself in people’s behaviour.
We look for resistance behaviour in eight different categories:
- Controlling behaviour
- Emotions
- Disengagement
- Work impact
- Acting out
- Negativity
- Building barriers
- Avoidance
Allow 5 minutes to brainstorm examples of resistance behaviour and note them in your workbook on page 3. Then upload your workbook to the assignment section below to proceed with your course. You can use this worksheet with your peers to proactively anticipate resistance and recognise it early.
Example
The Covid-19 pandemic forced a global change upon each country, organisations, and individual. A wide variety of resistance behaviour could be observed.

- Examples for controlling behaviours are asking inquisitive questions, influencing outcomes, defending the current state, using your status for your own agenda, e.g.
during the Covid-19 outbreak D. Trump used the term China-Virus to support his anti-china politics.
- Examples of emotional behaviours are anxiety, fear, grief, sadness, anger, frustration and depression, e.g. the social media coverage of the pandemic caused a global mass panic that manifested in hoarding toilet paper.
- Examples of disengagement include becoming silent, ignoring communications, indifference, apathy, low morale, focus on self, e.g. the level of emotional isolation and distance increased between people.
- Examples of work impact include reduced productivity, non-compliance, absenteeism, mistakes, e.g. the constant Covid-19 broadcast distracted employees from focussing on their daily routines.
- Examples of acting out include open conflict, arguments, sabotage, ill-tempered, passive, or actively aggressive behaviour, e.g. Supermarkets reported anti-social behaviour by patrons towards their staff when toilet paper became scarce.
- Examples of negativity include rumours, miscommunications, complaining, focus on problems, celebrating failure, e.g. WHO had to fight fake news circulating the internet.
- Examples of avoidance include ignoring the changes, reverting to old behaviours, workarounds, refusals to take responsibility, e.g. some countries had to tighten their rules because people hosted anti-corona parties.
- Examples of building barriers include excuses, counter-approaches, recruiting dissenters, secrecy and breakdown in trust, e.g. People like D.L. Katz, founding director of the Yale-Griffin Prevention Research Centre, believes that the lockdown might be a mistake possibly graver than the direct toll of the virus itself.
